Theory Of Natural Selection Definition Biology
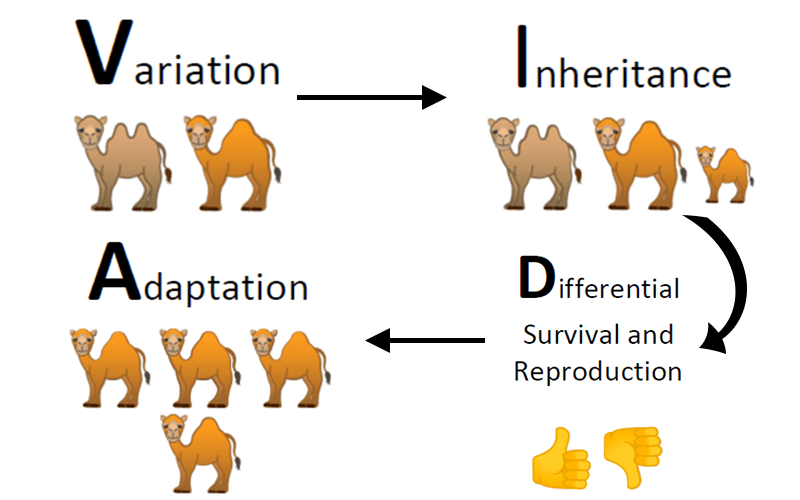
The theory of natural selection, first proposed by Charles Darwin, is a fundamental concept in biology that explains the diversity of life on Earth. It states that individuals with traits that make them better adapted to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing on their advantageous traits to their offspring. Over time, this process leads to the accumulation of beneficial traits within a population, resulting in the evolution of new species.
Natural selection operates through three main principles: variation, inheritance, and selection. Variation refers to the differences between individuals within a population, which can arise from genetic mutations or other sources. Inheritance refers to the passing on of traits from parents to offspring through genes. Selection refers to the process by which individuals with traits that make them better adapted to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce.
One of the key implications of natural selection is that it can lead to the adaptation of populations to their specific environments. This process is known as adaptive radiation, and it can result in the evolution of new species that are specialized for particular ecological niches. For example, the Galapagos finches studied by Darwin evolved different beak shapes and sizes in response to the different food sources available on each island.
The theory of natural selection provides a compelling explanation for the diversity of life on Earth and has revolutionized our understanding of biology. It has also been applied to other fields, such as psychology and economics, to explain the evolution of complex behaviors and social structures.
Post a Comment for "Theory Of Natural Selection Definition Biology"